Ovarian Cysts Diagnosis & Treatment
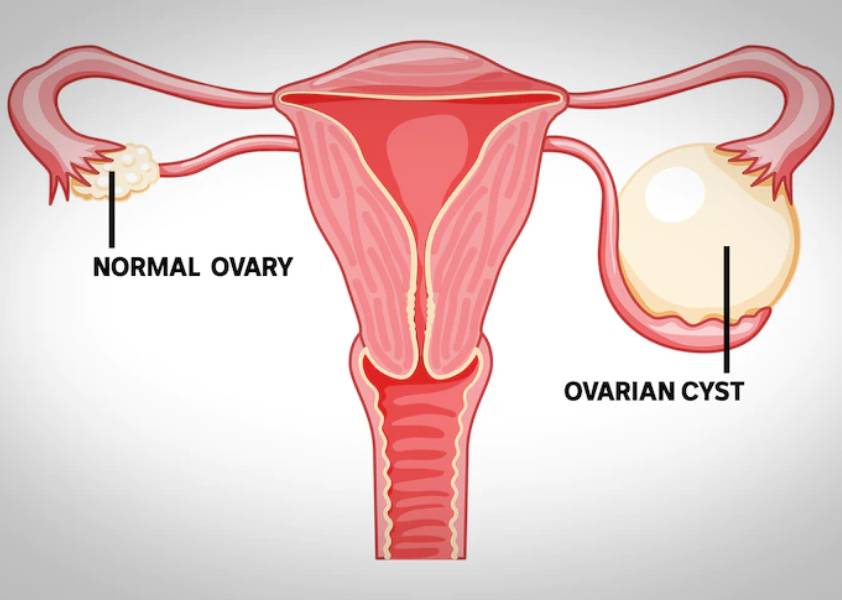
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
We understand that dealing with medical terms and conditions can be confusing, so lets understand …
What Are Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can develop on or within the ovaries, which are a part of the female reproductive system. These cysts are surprisingly common and can occur at any age, from adolescence to menopause.
Types of Ovarian Cysts:
Functional Cysts: These are the most common and often harmless. They form during a woman’s menstrual cycle and typically go away on their own.
Dermoid Cysts: These are a bit more unusual as they can contain various types of tissues like hair, skin, and even teeth! But don’t worry; they are usually benign.
Cystadenomas: These cysts develop on the surface of the ovary and may contain watery or mucous-like material. They can grow quite large, and need clinical evaluation.
Endometriomas: These cysts are associated with endometriosis, a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside of it. These cysts can be painful.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can result in multiple small cysts(which are nothing but eggs ) in the ovaries. It can lead to irregular periods and other health issues.
Symptoms:
Ovarian cysts often don’t cause any symptoms and are discovered during routine pelvic exams or ultrasounds. However, when symptoms do manifest, they may include:
- Bloating
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Irregular periods , heavy bleeding .
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty getting pregnant
Diagnosis:
If your doctor suspects you have an ovarian cyst, they may recommend:
- Pelvic ultrasound: This helps visualize the cyst and its characteristics.
- Blood tests: To check hormone levels and rule out certain conditions.
Treatment:
The treatment for ovarian cysts depends on various factors, including the type, size, and whether you’re experiencing any symptoms. Options may include:
- Watchful waiting: If the cyst is small and doesn’t cause symptoms, your doctor may suggest regular monitoring.
- Medications: Hormonal birth control pills can help resolve certain cysts .
- Surgery: If the cyst is large, causing pain, or appears suspicious, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove it.
Conclusion:
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any symptoms or have concerns. They can offer guidance tailored to your unique situation.
